Innovation in Aircraft Design
Overview of innovative approaches in aviation
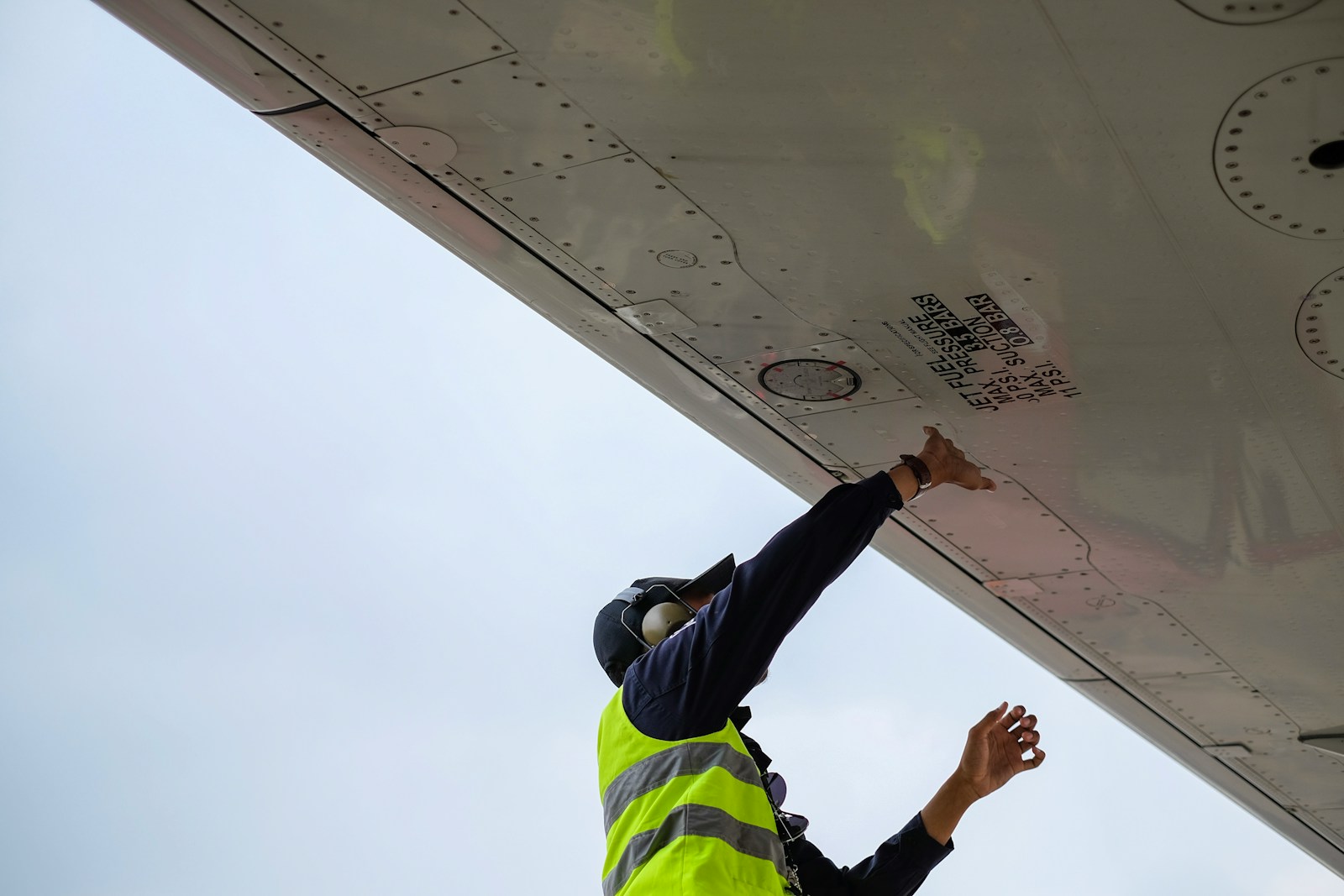

Efficiency: Fuel-efficient aerodynamics and materials
Maximizing fuel efficiency is a cornerstone of modern aircraft design, directly impacting operational costs and environmental sustainability. By utilizing advanced aerodynamics, such as optimized wing shapes, blended winglets, and laminar flow control, aircraft can reduce drag and improve overall performance. Additionally, incorporating lightweight composite materials, such as carbon fiber and titanium alloys, significantly lowers the aircraft's weight without compromising strength and durability. These innovations not only enhance fuel economy but also extend the aircraft's range, reduce emissions, and lower maintenance costs, making them essential for both commercial and military aviation.
Maintenance: Designing Aircraft with Lower Servicing Costs
Reducing maintenance costs is a key factor in designing efficient aircraft, ensuring long-term operational reliability while minimizing downtime. By integrating modular components and easily accessible systems, maintenance crews can quickly perform inspections, repairs, and part replacements with minimal disruption. Using durable, wear-resistant materials extends the lifespan of critical components, reducing the frequency of overhauls. Additionally, predictive maintenance technologies, such as real-time diagnostics and AI-powered monitoring systems, help detect potential issues before they become costly failures. These innovations collectively lower servicing costs, enhance safety, and improve aircraft availability for both commercial and military applications.
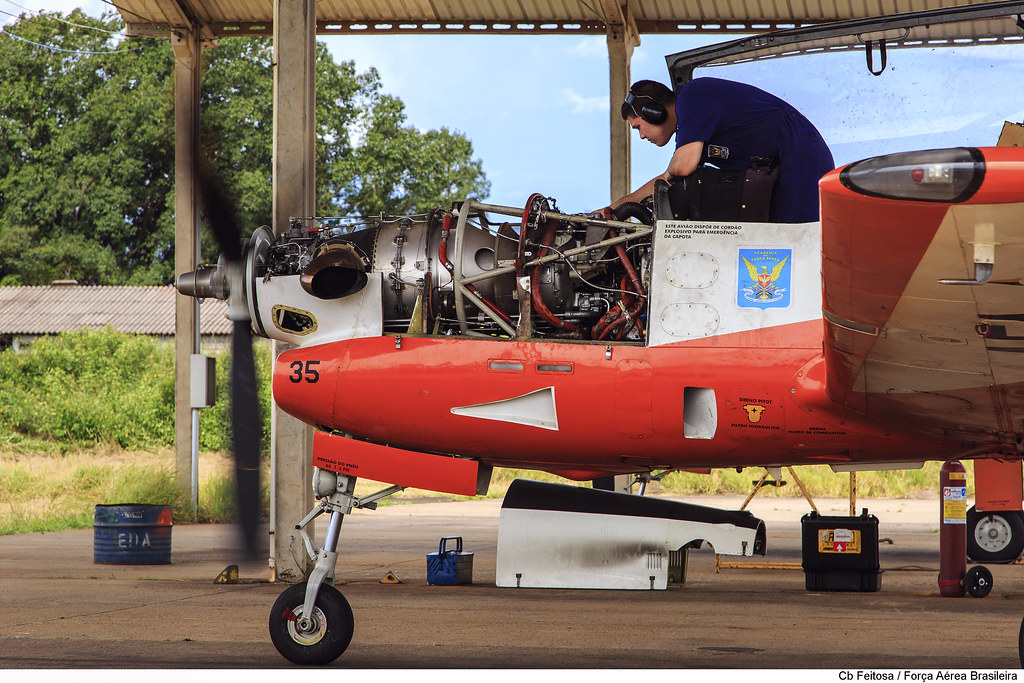

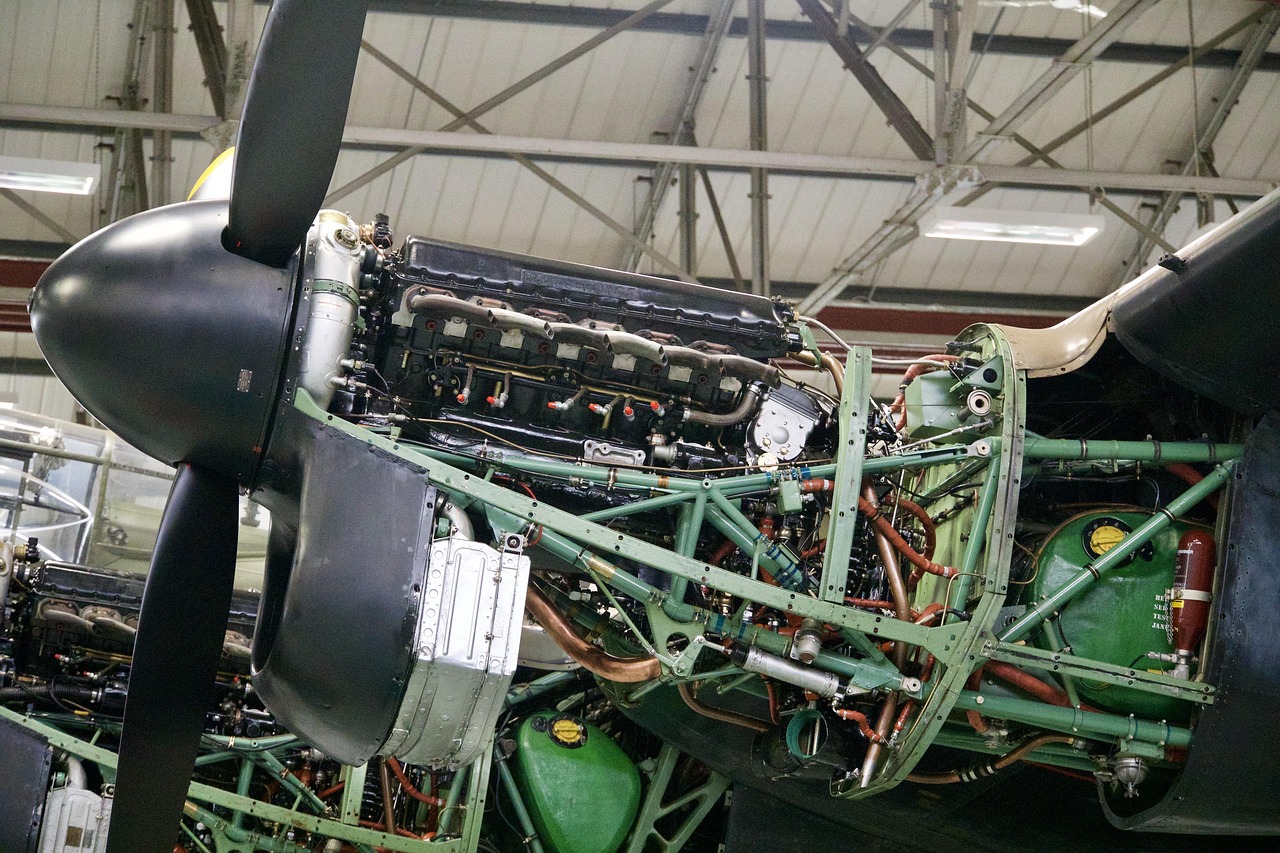
Durability: Long Operational Life to Reduce Replacement and Repair Costs
Aircraft durability is a critical factor in minimizing long-term operating expenses and ensuring sustained performance over years of service. By utilizing advanced materials such as corrosion-resistant alloys and high-strength composites, modern aircraft can withstand harsh environmental conditions and heavy operational use. Structural reinforcements and fatigue-resistant designs further enhance longevity, reducing the need for frequent repairs or component replacements. Additionally, advanced coatings and surface treatments protect against wear, weathering, and chemical exposure. By prioritizing durability in aircraft design, operators benefit from lower lifecycle costs, extended service intervals, and improved reliability across various mission profiles
